Routine review of Workspace storage not only helps an administrator identify major changes to individual and shared drive storage usage but also ensures that accounts remain below storage limits.
A Google Workspace administrator has at least two important reasons to track Workspace storage usage: To monitor usage compared to storage limits and to identify major usage changes. Workspace administrators may especially want to monitor usage if the organization is on a plan such as Google Workspace Business Starter, which limits storage to 30 GB per user.
While 30 GB may be sufficient for many purposes, it’s significantly less than the pooled storage of 2 TB per user, 5 TB per user or the essentially unlimited storage available on other plans. Total usage includes not only Drive storage, but also email and photo storage.
Periodic monitoring of storage also may alert an administrator to changes in individual or shared drive storage usage. A sudden increase in storage usage might be due to accidental data deletion, for example, while a significant decrease could signal a massive transfer of video files. Either change may merit additional inquiry and discussion.
These sorts of storage usage changes remain a concern, even when storage limits in and of themselves are not a constraint, such as on Workspace Enterprise plans, which offer as much storage as your organization needs.
SEE: Hiring Kit: Cloud Engineer (TechRepublic Premium)
How to review Google Workspace storage
To review and manage storage, a Google Workspace administrator with appropriate permissions will want to sign in to the Admin console and then select Storage — either from the left-side menu or the Storage box on the main dashboard.
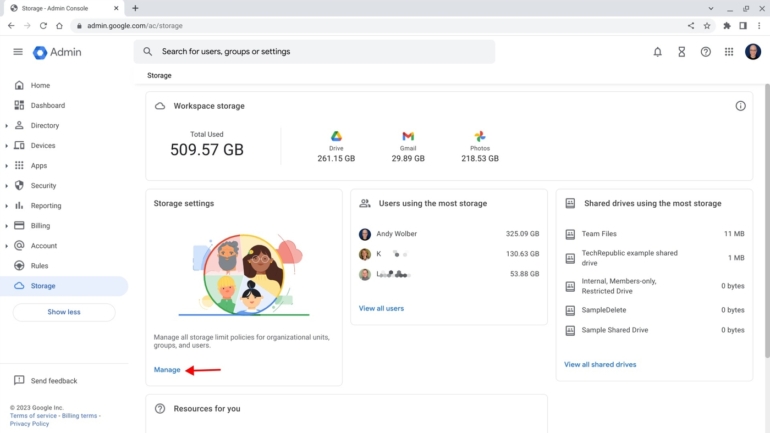
In the Admin console, the Storage section displays the total storage used with a summary of data stored on specific services, such as Google Drive, Gmail and Photos, as shown in Figure A. Two sub-panels list the largest usage of storage. One is sorted by user accounts and the other by Shared drives. This helps you identify particular people and teams using significant storage.
Figure A
I suggest an administrator review this information monthly. This routine check might help identify any major changes in time for accidentally deleted data to be recovered easily, since most Google services retain data moved to the trash for 30 days.
How to set Google Workspace storage limits
Select Manage, as indicated by the arrow in Figure A, if you wish to configure storage limits for your organization. You can manage limits for each organizational unit separately. For example, you may prefer to set no limits for full-time employees but choose to configure storage limits for an organizational unit configured with all part-time or temporary employees. Similarly, a school administrator might choose to set different limits for teachers, staff or students.
First, make sure you have selected the desired organizational unit, as in Figure B, where the column with Users, Groups and Organizational Units is shown.
Figure B
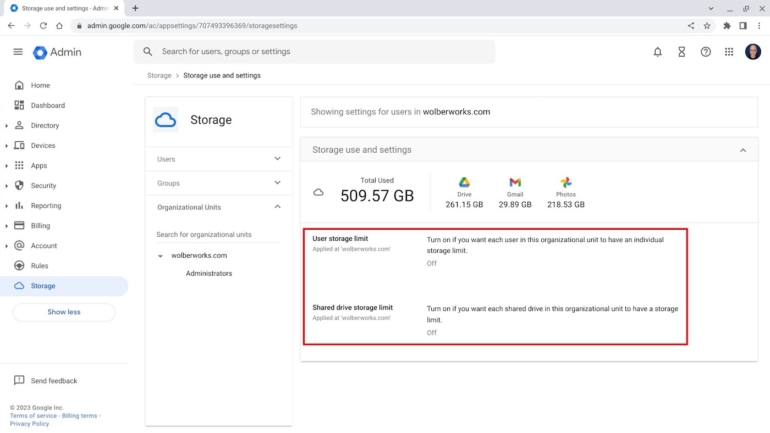
Next, you may enable limits either for users or shared drives. The user storage limit allows you to ensure that no individual user in the selected organizational unit may exceed a specified amount of storage. Remember, the limit is the total data saved across an account’s Google Drive, Gmail, Photos and other Workspace-associated apps.
Alternatively, you may choose to constrain the size of data stored on shared drives for the selected organizational unit. A limit on shared drive size might be helpful to ensure that teams don’t use shared drives for significant amounts of data. In some cases, this might be of particular concern to organizations that rely on shared drives for external collaboration.
What’s your experience with Workspace storage?
If you’re a Google Workspace administrator, how often do you review storage usage for your organization? Have you chosen to configure any storage constraints for any portion of your organization — either for sets of users or shared drives? How often do you contact individual users or shared drive managers to discuss significant storage changes identified as a result of routine storage reviews? Mention or message me on Mastodon (@awolber) to let me know how you monitor and manage Google Workspace storage for your organization.
